Forex Volatility: How to Navigate Market Swings Effectively
Have you ever noticed how currency prices can rise and fall quickly? As such, Forex traders got excited but sometimes nervous? That’s Forex volatility—an important part of trading. Traders need to understand volatility because it can greatly affect their profits and losses.
In this article, we’ll explore what Forex volatility is, why it matters, and how you can measure and handle it.
Forex Volatility Explained
Forex volatility measures how much and how fast currency prices change in the foreign exchange market volatility.
This is a crucial concept for traders to grasp. It’s because it determines their approach to managing risks and maximizing returns.
For traders, understanding this helps in balancing risks and rewards.
Think of it like the market’s mood swings. Prices may move only a little on some days, while on others, they swing wildly. For example, with the EUR/USD pair:
- On a calm day, it might move from 1.1000 to 1.1010.
- On a more volatile day, it could swing from 1.1000 to 1.1100 or even more.
These changes show how dynamic Forex markets can be, offering both risks and opportunities.
Factors That Affect Forex Volatility
Many things can make the Forex market more or less volatile. These are often grouped into two categories:
Economic Factors:
- Economic Data Releases: Reports like unemployment rates, GDP, or inflation can make prices change quickly.
- Central Bank Decisions: Changes to interest rates or monetary policies often cause big market movements.
Non-Economic Factors:
- Political Events: Elections or political tensions can lead to unpredictable price changes.
- Natural Disasters: Events like earthquakes or hurricanes can create sudden volatility.
- Market Sentiment: Traders’ emotions and speculations often amplify price movements.
Example: If the U.S. unemployment rate suddenly increases, the USD might weaken, causing pairs like EUR/USD to go up.
On the other hand, a strong GDP report in China could boost the CNY. As a result, this affects pairs like USD/CNY or AUD/CNY.
Forex Volatility Chart
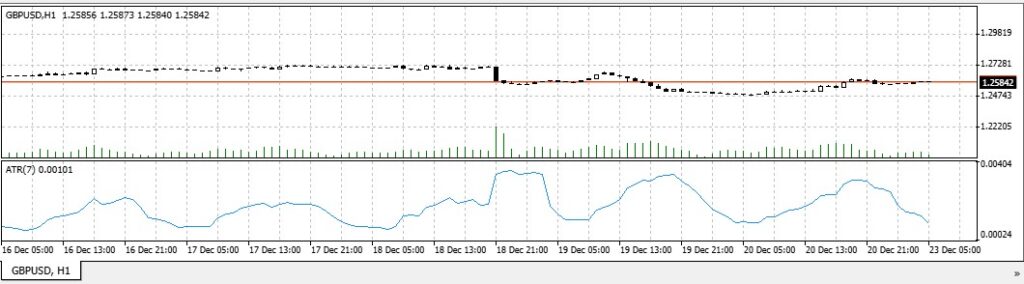
Source: Sample GBP/USD pair traded on a 7-day timeframe and using Average True Range indicator.
A Forex volatility chart is a visual tool that helps traders understand price movements in real time.
These charts can display key forex volatility indicators like ATR, Bollinger Bands, or price changes over a specific period, giving traders a clear picture of market activity.
A forex volatility chart simplifies the process of identifying high and low volatility trends visually.
Another example of a Forex Volatility Chart:
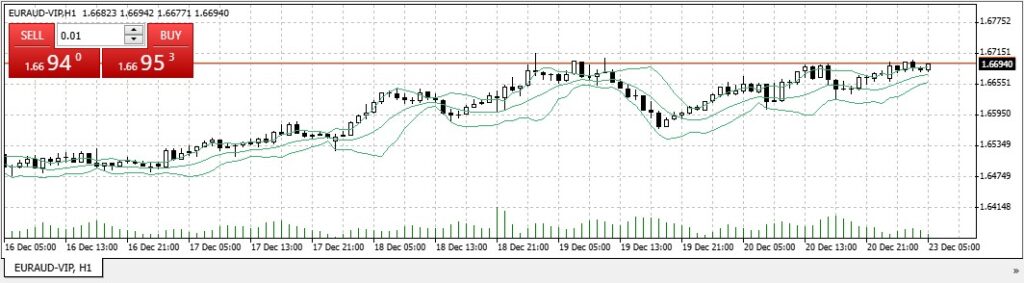
Source: Bolinger Bands indicator on EUR/AUD
Let’s suppose a chart showing EUR/AUD price movements over a week.
On days with low volatility, the price fluctuates within a narrow range, represented by closely packed candlesticks.
On high-volatility days, the range widens significantly, with larger candlesticks showing dramatic price shifts.
Overlaying Bollinger Bands on the chart can further highlight these differences. Thus, this makes it easier to identify potential trading opportunities.
Forex Volatility Formula
Traders often rely on formulas. The volatility formula serves to quantify volatility and make better trading decisions.
One widely used method is the Standard Deviation Formula. It calculates how much currency prices vary from their average over a specific period.
Standard Deviation Formula: σ = √(Σ(Pi – P̄)² / N)
Where:
- σ = Standard deviation (volatility measure)
- Pi = Each price in the dataset
- P̄ = Average price
N = Total number of prices
Example: Let’s say the closing prices of EUR/USD for 5 days are: 1.1000, 1.1050, 1.1020, 1.1080, and 1.1030.
- Calculate the average price: P̄ = (1.1000 + 1.1050 + 1.1020 + 1.1080 + 1.1030) / 5 = 1.1036
- Calculate each squared deviation from the average: (1.1000 – 1.1036)², (1.1050 – 1.1036)², and so on.
- Compute the standard deviation: σ = √(sum of squared deviations / 5)
Using this formula, traders can numerically assess market volatility and use it to refine their strategies.
For example:
If the calculated standard deviation is below 0.5% of the average price, it indicates low volatility. This means the market is relatively stable.
On the other hand, a standard deviation above 1% reflects high volatility. Therefore, this signals rapid price changes and greater risk and opportunity.
Forex Market Volatility Index
The Forex Market Volatility Index (VIX) plays a critical role in measuring market uncertainty. Hence, it assists traders align their strategies with current conditions.
While traditionally associated with stock markets, similar indices can be used in Forex to gauge market sentiment and predict price movements.
How It Works: The Volatility Index tracks implied volatility based on options pricing, providing a real-time gauge of traders’ expectations for future price fluctuations.
Example in Forex:
Consider a hypothetical Forex VIX measuring volatility for major currency pairs like EUR/USD and GBP/USD.
A rising index value signals increasing uncertainty and potential for sharper price movements, while a falling value suggests a calmer market.
Why It Matters:
- Risk Management: Traders can use the index to decide when to reduce position sizes or avoid overleveraging.
- Opportunity Identification: Higher volatility often correlates with increased trading opportunities.
By monitoring such indices, traders can align their strategies with current market conditions.
Forex High Volatility Pairs
Certain currency pairs are known for their high volatility, often experiencing larger and faster price swings compared to others.
These forex high volatility pairs are popular among traders seeking significant profit opportunities. But, they also come with increased risks, requiring careful planning and strategy.
Examples of High Volatility Pairs:
- GBP/JPY (British Pound / Japanese Yen): Known as “The Dragon,” this pair is famous for its wide price ranges and sharp movements, driven by economic differences between the UK and Japan.
2. EUR/AUD (Euro / Australian Dollar): This pair’s volatility often arises from divergent economic conditions and commodity price fluctuations affecting the Australian dollar.
3. USD/ZAR (US Dollar / South African Rand): A highly volatile pair influenced by global risk sentiment, political events in South Africa, and commodity prices like gold.
4. AUD/JPY (Australian Dollar / Japanese Yen): With the Australian dollar linked to commodities and the Japanese yen considered a safe haven, this pair is highly sensitive to market sentiment and global events.
How Volatility Impacts Forex Trading
Volatility can be both good and bad for traders. Here’s why:
Benefits:
- Profit Opportunities: Traders can take advantage of large price swings.
- Faster Price Changes: Quick movements mean faster potential gains.
Drawbacks:
- Higher Risks: Rapid changes can lead to unexpected losses.
- Wider Spreads: It may cost more to trade during volatile periods.
Example: Imagine trading EUR/USD. In a volatile market, a trade could go from a 20-pip profit to a 30-pip loss in minutes. However, if timed right, a volatile market could also lead to quick gains.
Strategies to Handle Forex Volatility
Managing volatility is key to success in Forex trading. Here are some tips:
- Use Stop-Loss Orders: Automatically close trades if the market moves too far against you. For instance, if you buy EUR/USD at 1.1000, you might set a stop-loss at 1.0980 to limit losses.
2. Adjust Trade Sizes: During volatile times, trade smaller amounts to lower your risk. If your usual trade is $10,000, you might lower it to $5,000 when volatility increases.
3. Set Volatility-Based Exits: Use tools like ATR to decide when to exit. For example, if ATR for EUR/USD is 20 pips, you could exit a trade if prices move 30 pips (1.5 x ATR) against you.
4. Trade During Quieter Hours: Some sessions, like the European one, tend to have steadier price movements compared to others.
5. Stay Informed: Keep track of news and events, such as interest rate decisions, that might cause volatility.
Example Tip:
During the 2020 U.S. elections, USD pairs became very volatile. Traders who monitored the news and adjusted their strategies managed to minimize losses and find profitable opportunities.
Conclusion
Understanding Forex volatility helps traders find opportunities and control risks. By using tools and strategies to handle it, you can trade with more confidence.
Remember, volatility is a natural part of the market—not something to fear. Start learning and practicing today with StyleForex.com to get expert tips, insights, and tools that help you succeed in Forex trading.